Patch Clamp Whole Cell Tecnica
• The voltage clamp is an experimental method used by to measure the through the of excitable cells, such as, while holding the membrane at a set level. A basic voltage clamp will iteratively measure the, and then change the membrane potential (voltage) to a desired value by adding the necessary current. This 'clamps' the cell membrane at a desired constant voltage, allowing the voltage clamp to record what currents are delivered. Because the currents applied to the cell must be equal to (and opposite in to) the current going across the cell membrane at the set voltage, the recorded currents indicate how the cell reacts to changes in membrane potential. Cell membranes of excitable cells contain many different kinds of, some of which are. The voltage clamp allows the membrane voltage to be manipulated independently of the ionic currents, allowing the relationships of membrane channels to be studied. Contents • • • • • • • • • • History [ ] The concept of the voltage clamp is attributed to and in the spring of 1947.
Autodesk Inventor 2014 Keygen Crack Software. They inserted an internal electrode into the giant axon of a squid and began to apply a current. Cole discovered that it was possible to use two and a to keep the at a level set by the experimenter. Cole developed the voltage clamp technique before the era of, so his two electrodes consisted of fine wires twisted around an rod.
Because this type of electrode could be inserted into only the largest cells, early electrophysiological experiments were conducted almost exclusively on axons. A personal photo of Kenneth Cole, given to Dr. Enfermagem Pediatrica Wong Pdf more. Walter Woodbury Squids squirt jets of water when they need to move quickly, as when escaping a predator. To make this escape as fast as possible, they have an that can reach 1 mm in diameter (signals propagate more quickly down large axons). The was the first preparation that could be used to voltage clamp a transmembrane current, and it was the basis of Hodgkin and Huxley's pioneering experiments on the properties of the action potential. Realized that, to understand ion flux across the membrane, it was necessary to eliminate differences in membrane potential. Using experiments with the voltage clamp, Hodgkin and published 5 papers in the summer of 1952 describing how ionic currents give rise to the.
The final paper proposed the which mathematically describes the action potential. The use of voltage clamps in their experiments to study and model the action potential in detail has laid the foundation for; for which they shared the 1963. Technique [ ] The voltage clamp is a current generator. Is recorded through a 'voltage electrode', relative to, and a 'current electrode' passes current into the cell. The experimenter sets a 'holding voltage', or 'command potential', and the voltage clamp uses negative feedback to maintain the cell at this voltage. The electrodes are connected to an amplifier, which measures membrane potential and feeds the signal into a.
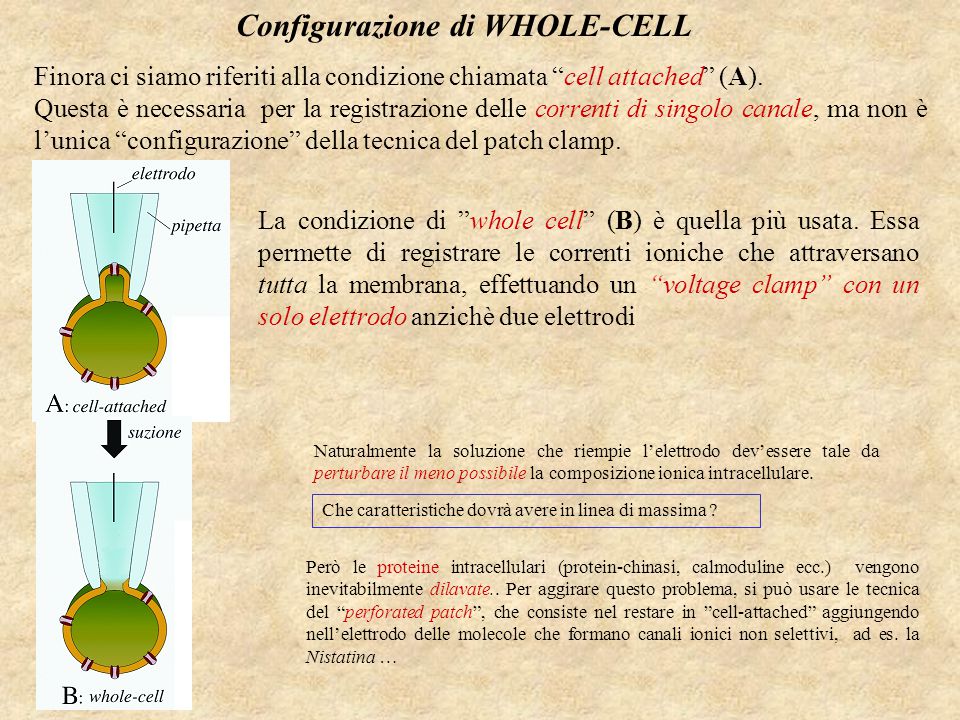
The advantage of whole-cell patch clamp recording over sharp electrode technique recording is that the larger opening at the tip of the patch clamp electrode. Iss Pyaar Ko Kya Naam Doon Season 1 Episode 200. Whole-cell patch clamp is a valuable tool for measuring the response of single cells to stimuli. Furthermore, paired recordings can be used to investigate the impact of neuron firing on excitable target cells, like muscle.
This amplifier also gets an input from the signal generator that determines the command potential, and it subtracts the membrane potential from the command potential (V command – V m), magnifies any difference, and sends an output to the current electrode. Whenever the cell deviates from the holding voltage, the generates an 'error signal', that is the difference between the command potential and the actual voltage of the cell. The passes current into the cell to reduce the error signal to zero. Thus, the clamp circuit produces a current equal and opposite to the ionic current. Variations of the voltage clamp technique [ ] Two-electrode voltage clamp using microelectrodes [ ]. Two-electrode voltage clamp The two-electrode voltage clamp (TEVC) technique is used to study properties of membrane proteins, especially ion channels. Researchers use this method most commonly to investigate membrane structures expressed in.
The large size of these oocytes allows for easy handling and manipulability. The TEVC method utilizes two low-resistance pipettes, one sensing voltage and the other injecting current. The microelectrodes are filled with conductive solution and inserted into the cell to artificially control membrane potential. The membrane acts as a as well as a, while the fluids on either side of the membrane function as. The microelectrodes compare the membrane potential against a command voltage, giving an accurate reproduction of the currents flowing across the membrane. Current readings can be used to analyze the electrical response of the cell to different applications. This technique is favored over single-microelectrode clamp or other voltage clamp techniques when conditions call for resolving large currents.